Associação Portuguesa de Investigação em Cancro
Immunosensor for the analysis HER2 ECD
Immunosensor for the analysis HER2 ECD
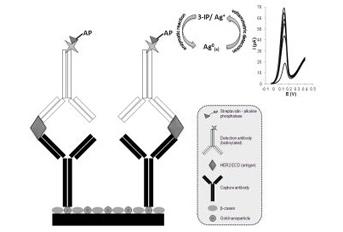
An electrochemical immunosensor for the analysis of HER2 ECD in human serum samples was developed. To achieve this goal a screen-printed carbon electrode, modified with gold nanoparticles, was used as transducer surface. A sandwich immunoassay, using two monoclonal antibodies, was employed and the detection of the antibody-antigen interaction was performed through the analysis of an enzymatic reaction product by linear sweep voltammetry. The calibration curve was established between 15 and 100 ng/mL and a limit of detection of 4.4 ng/mL was achieved. These results indicate that the developed immunosensor could be a promising tool in breast cancer diagnostics, patient follow-up and monitoring of metastatic breast cancer.
Raquel C.B. Marques1, Subramanian Viswanathan2, Henri P.A. Nouws1, Cristina Delerue-Matos1, M. Begoña González-García1
1 REQUIMTE, Instituto Superior de Engenharia do Porto, Instituto Politécnico do Porto, Rua Dr. António Bernardino de Almeida 431, 4200-072 Porto, Portugal
2 Department of Industrial Chemistry, Alagappa University, Karaikudi-630003, Tamilnadu, India
Human epidermal growth factor receptor2 (HER2) is a breast cancer biomarker that plays a major role in promoting breast cancer cell proliferation and malignant growth. The extra cellular domain (ECD) of HER2 can be shed into the blood stream and its concentration is measurable in the serum fraction of blood. In this work an electrochemical immunosensor for the analysis of HER2 ECD in human serum samples was developed. To achieve this goal a screen-printed carbon electrode, modified with gold nanoparticles, was used as transducer surface. A sandwich immunoassay, using two monoclonal antibodies, was employed and the detection of the antibody–antigen interaction was performed through the analysis of an enzymatic reaction product by linear sweep voltammetry. Using the optimized experimental conditions the calibration curve (ip vs. log[HER2ECD]) was established between 15 and 100 ng/mL and a limit of detection (LOD) of 4.4 ng/mL was achieved. These results indicate that the developed immunosensor could be a promising tool in breast cancer diagnostics, patient follow-up and monitoring of metastatic breast cancer since it allows quantification in a useful concentration range and has an LOD below the established cut-off value (15 ng/mL).
Talanta 129 (2014) 594-599




