Associação Portuguesa de Investigação em Cancro
Gold and Light: A Promising Approach for Melanoma Treatment
Gold and Light: A Promising Approach for Melanoma Treatment
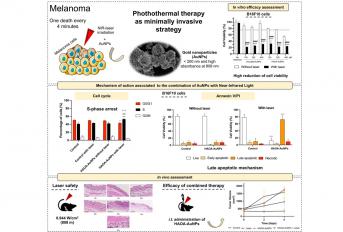
The study "Combination of gold nanoparticles with near-infrared light as an alternative approach for melanoma management" investigated the combination of gold nanoparticles with near-infrared laser irradiation as a promising therapeutic strategy for melanoma treatment. The different assays conducted demonstrated nanoparticles or the laser alone did not cause significant cytotoxic effects. In contrast, the combined therapy substantially reduced cell viability and induced cell death through an apoptotic mechanism. Additionally, in vivo tests in animal models showed that a single intratumoral administration of gold nanoparticles followed by three laser irradiations, on alternate days, delayed tumor progression, highlighting the great potential of this approach to the treatment of localized and superficial tumors like melanoma.
Authors and Affiliations:
Joana Lopesa, Carla M. Rodriguesb, Ana Godinho-Santosa, João M. P. Coelhoc, Luís C. Cabaçod, Duarte C. Barrald, Pedro Faíscae, José Catarinof,g, Daniela Nunesh, Elvira Fortunatoh, Rodrigo Martinsh, Cecília M. P. Rodriguesa, Maria Manuela Gaspara,c,* and Catarina Pinto Reisa,c,*
a Research Institute for Medicines (iMed.ULisboa), Faculty of Pharmacy, Universidade de Lisboa, Av. Professor Gama Pinto, 1649-003 Lisboa, Portugal;
b REQUIMTE - LAQV, Chemistry Department, NOVA School of Science and Technology, NOVA University Lisbon, Campus da Caparica, 2829-516 Caparica, Portugal;
c Instituto de Biofísica e Engenharia Biomédica (IBEB), Faculdade de Ciências, Universidade de Lisboa, Campo Grande 1749-016 Lisboa, Portugal;
d iNOVA4Health, NOVA Medical School, Faculdade de Ciências Médicas, NMS, FCM, Universidade NOVA de Lisboa, Campo dos Mártires da Pátria, 130, 1169-056 Lisboa, Portugal;
e CECAV- Centro de Ciência Animal e Veterinária- Faculdade de Medicina Veterinária de Lisboa- Universidade Lusófona-Centro Universitário de Lisboa, Portugal;
f Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Universidade Lusófona-Centro Universitário de Lisboa, Portugal;
g School of Animal Health, Protection and Welfare, Lusophone Polytechnic Institute, Lisbon, Portugal;
h Department of Materials Science, NOVA School of Science and Technology, Campus de Caparica, i3N/CENIMAT, 2829-516 Caparica, Portugal;
Abstract:
Melanoma is the most aggressive type of skin cancer and recently approved drugs are often associated with resistance and significant adverse effects. Therefore, the design of more effective and safe options remains imperative. Photothermal therapy (PTT) using gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) presents a promising and innovative approach. In this work, the efficacy of combining a previously optimized formulation of AuNPs coated with a mixture of hyaluronic and oleic acids (HAOA-AuNPs) with near-infrared (NIR) laser irradiation in melanoma cell lines was explored. Coated and uncoated AuNPs formulations were characterized in physicochemical, morphological and elemental terms. Next, the cellular uptake efficiency as well as antiproliferative activity of the combination of each formulation with laser irradiation was evaluated. Subsequently, HAOA-AuNPs were selected to assess the underlying mechanism of combined therapy by cell cycle and Annexin V/PI assays. An in vivo syngeneic murine melanoma model was also conducted. In vitro studies demonstrated that 24 h after incubation and in the absence of laser, HAOA-AuNPs did not exhibit cytotoxic effects on the melanoma cell lines tested, similar to the laser alone. On the contrary, the combination therapy resulted in a large reduction in cell viability. Furthermore, it has been shown to promote S-phase cell cycle arrest and increase in the percentage of late apoptotic cells. Finally, the in vivo proof-of-concept showed that the intratumoral administration of HAOA-AuNPs followed by three laser irradiations impaired tumor progression. Collectively, AuNP-based PTT holds significant potential to improve treatment efficacy and safety, offering a versatile and potent tool against cancer.
Journal: International Journal of Pharmaceutics
Link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378517324011864?via%3Dihub




