Associação Portuguesa de Investigação em Cancro
Portuguese group combine nanoparticle delivery of gene therapy and standard chemotherapy to overcome leukemia
Portuguese group combine nanoparticle delivery of gene therapy and standard chemotherapy to overcome leukemia
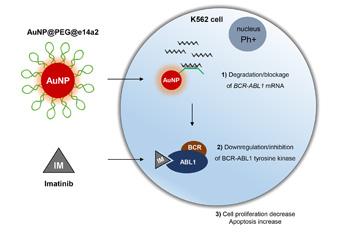
Specific gene silencing was vectorized via gold nanoparticles to enhance the killing potential of chemotherapy against leukemia cells. By targeting the fusion oncogene BCR-ABL1 using gold nanoaprticles in chronic myeloid leukemia cells, the Portuguese researchers were capable to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of standard chemotherapy in a combined strategy that this groups has been optimizing at UCIBIO (Research Unit on Applied Molecular Biosciences), Faculdade de Ciências e Tecnologia of Universidade Nova de Lisboa. The combination of nanomedicine and standard chemotherapy allows to improve the killing of cancer cells in s selective process while decreasing side effects. This study highlight the potential of nanomedicine to circumvent drug resistance in leukemia cells.
Authors and Affiliations:
Raquel Vinhas1, Alexandra R. Fernandes1, Pedro V. Baptista1
1 UCIBIO, Departamento de Ciências da Vida, Faculdade de Ciências e Tecnologia, Universidade Nova de Lisboa
Abstract:
Introduction of tyrosine kinase inhibitors for chronic myeloid leukemia treatment is associated to a 63% probability of maintaining a complete cytogenetic response, meaning that over 30% patients require an alternative methodology to overcome resistance, tolerance or side-effects. Considering the potential of nanotechnology in cancer treatment and the benefits of a combined therapy with imatinib, a nanoconjugate was designed to achieve BCR-ABL1 gene silencing. Gold-nanoparticles were functionalized with a single-stranded DNA oligonucleotide that selectively targets the e14a2 BCR-ABL1 transcript expressed by K562 cells. This gold-nanoconjugate showed great efficacy in gene silencing that induced a significant increase in cell death. Variation of Bcl-2 and Bax protein expression, increase on caspase-3 activity and apoptotic bodies in cells treated with the nanoconjugate demonstrate its aptitude to induce apoptosis on K562 BCR-ABL1-expressing cells. Moreover, combination of the silencing gold-nanoconjugate with imatinib prompted a decrease of imatinib IC50. This Au-nanoconjugate was also capable of inducing the loss of viability of imatinib-resistant K562 cells. This strategy shows that combination of gold-nanoconjugate and imatinib make K562 cells more vulnerable to chemotherapy and that the Au-nanoconjugate alone may overcome imatinib resistance mechanisms, thus providing an effective treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia patients that exhibit drug tolerance.
Journal: Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids
Link: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2162253117301737?via%3Dihub




