Associação Portuguesa de Investigação em Cancro
Potential small-molecule activators of caspase-7 identified using yeast-based caspase-3 and -7 screening assays
Potential small-molecule activators of caspase-7 identified using yeast-based caspase-3 and -7 screening assays
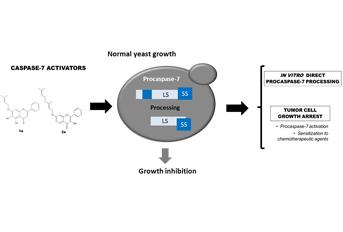
Caspases-3 and -7 play a key role in the activation of apoptosis, and therefore the search for activators of these proteases has therefore deserved particular attention in the field of antineoplasic drug discovery. This work describes the implementation of a screening system for activators of these human caspases based on yeast, a unicellular eukaryotic organism, as a simplified cell model for large-scale research. Using this approach we identified two new potential activators of caspase-7, which did not interfere with the activity of caspase-3 in yeast. The activity of these compounds was further confirmed in two human tumor cell lines.
Authors and Afiliations:
Pereira C1, Lopes-Rodrigues V2, Coutinho I1, Neves MP3, Lima RT2, Pinto M3, Cidade H3, Vasconcelos MH4, Saraiva L5 (# contributed equally to this work)
1REQUIMTE, Faculdade de Farmácia, Universidade do Porto, Rua de Jorge Viterbo Ferreira no. 228, 4050-313 Porto, Portugal; Laboratório de Microbiologia, Departamento de Ciências Biológicas, Faculdade de Farmácia, Universidade do Porto, Rua de Jorge Viterbo Ferreira no. 228, 4050-313 Porto, Portugal.
2Cancer Drug Resistance Group, IPATIMUP - Instituto de Patologia e Imunologia Molecular da Universidade do Porto, Rua Doutor Roberto Frias, 4200 Porto, Portugal; Centro Interdisciplinar de Investigação Marinha e Ambiental (CIIMAR), Universidade do Porto, Rua dos Bragas n° 289, 4050-123 Porto, Portugal.
3Centro Interdisciplinar de Investigação Marinha e Ambiental (CIIMAR), Universidade do Porto, Rua dos Bragas n° 289, 4050-123 Porto, Portugal; Centro de Química Medicinal da Universidade do Porto (CEQUIMED-UP), and Laboratório de Química Orgânica e Farmacêutica, Departamento de Ciências Químicas, Faculdade de Farmácia, Universidade do Porto, Rua Jorge Viterbo Ferreira n° 228, 4050-313 Porto, Portugal.
4Laboratório de Microbiologia, Departamento de Ciências Biológicas, Faculdade de Farmácia, Universidade do Porto, Rua de Jorge Viterbo Ferreira no. 228, 4050-313 Porto, Portugal; Cancer Drug Resistance Group, IPATIMUP - Instituto de Patologia e Imunologia Molecular da Universidade do Porto, Rua Doutor Roberto Frias, 4200 Porto, Portugal.
5REQUIMTE, Faculdade de Farmácia, Universidade do Porto, Rua de Jorge Viterbo Ferreira no. 228, 4050-313 Porto, Portugal; Laboratório de Microbiologia, Departamento de Ciências Biológicas, Faculdade de Farmácia, Universidade do Porto, Rua de Jorge Viterbo Ferreira no. 228, 4050-313 Porto, Portugal.
Abstract:
Caspases-3 and -7 are at the core of the execution phase of apoptosis. The search for activators of these proteases has therefore deserved particular attention in the field of anticancer drug discovery. Here, a simplified yeast-based screening approach was developed and used to search for activators of caspases-3 and -7, followed by evaluation of the activity of the selected compounds in the human tumor cell lines HL-60 (acute promyelocytic leukemia) and MCF-7 (breast adenocarcinoma). By using the yeast approach, two potential activators of caspase-7, 5,6-dihydroxy-7-prenyloxyflavone (1a) and 3-hydroxy-7-geranyloxyflavone (2a), were identified. Unlike the known caspases-3 and -7 activator, the procaspase activating compound-1 (PAC-1), these flavonoids did not interfere with the caspase-3 activity in yeast. Moreover, flavonoids 1a and 2a processed procaspase-7 to the active caspase-7 both in yeast and in vitro processing assays, and inhibited the growth of HL-60 and MCF-7 human tumor cells with higher potencies than PAC-1, particularly in the absence of caspase-3 (MCF-7 cells). In MCF-7 cells, the flavonoids processed procaspase-7, increased its activity and sensitized these cells to the effects of the cytotoxic drug, etoposide. In conclusion, the developed yeast target-based screening assays led to the identification of potential caspase-7 activators. A proof of concept is therefore provided for the effectiveness of the yeast assays in the discovery of caspase activators. Additionally, the identified compounds may pave the way for a new class of caspase activators with improved anticancer properties.
Journal:
European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences
Link:
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0928098713004892




