Associação Portuguesa de Investigação em Cancro
Modelo computacional dos primeiros passos no desenvolvimento do cancro da bexiga
Modelo computacional dos primeiros passos no desenvolvimento do cancro da bexiga
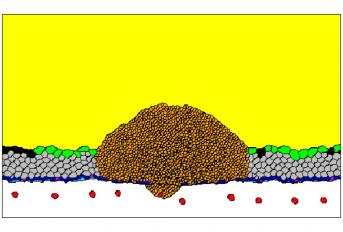
As propriedades mecânicas das células e do ambiente extracelular, in particular a sua rigidez e capacidade de adesão, são importantes nos primeiros passos de iniciação do cancro da bexiga. Um modelo computacional, desenvolvido na Universidade de Coimbra, descreve as diferentes camadas do urotélio e permite estudar quais as características mais relevantes para a capacidade invasiva dos tecidos vizinhos pelas células tumorais. Este trabalho fornece indicações úteis para o desenvolvimento de estratégias terapêuticas alternativas.
Autores e Afiliações:
João Carvalho, Valéria Lopes, Rui Travasso
CFisUC, Department of Physics, University of Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal
Abstract:
Bladder cancer is one of the most common types of cancer , being the sixth more frequent in men, and one with higher recurrence rates and overall treatment costs. We introduce an agent-based computational model of the urothelium, adopting a Cellular Potts Model (CPM) approach to describe both a healthy urothelium and the development of bladder cancer. We focus on the identification of the conditions in which cancer cells cross, by mechanical means, the basement membrane and invade the bladder lamina propria. When within the urothelium the tumor grows in a very constrained environment. These tight conditions imply that the urothelium layer where the tumor initiates greatly determines tumor growth and invasiveness. Moreover, we demonstrate how specific mechanical properties of the cancer cells, as their stiffness or the adhesion to neighboring cells, heavily modulate the critical initial moments of tumor development. We propose that these characteristics should be considered as therapeutic targets to control tumor growth.
Revista:
International Journal for Numerical Methods in Biomedical Engineering
Link:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/cnm.3417




